|
News
|
LCG, March 13, 2026--The Southwest Power Pool (SPP) announced yesterday that leaders from the participating organizations voted unanimously to proceed as planned with expanding its regional transmission organization (RTO) services into the Western Interconnection. SPP sees the decision to proceed as planned as a strong signal of confidence as SPP and its partner utilities prepare for this key milestone, which will occur overnight between March 31 and April 1.
Read more
|
|
LCG, March 6, 2026--Entergy yesterday announced approximately $5 billion in total savings for 2.3 million customers in Arkansas, Louisiana and Mississippi resulting from data center customer agreements in those states. Entergy, which completed its first data center customer agreement in 2024, projects the customer savings over the next 20 years and after the regulatory approval or acknowledgement of the public service commissions in those states.
Read more
|
|
|
Press Release
Impacts of High Variable Renewable Energy Futures
May 23, 2018 -- Lawrence Berkeley Lab partnered with LCG Consulting to develop a large number of variable renewable energy (VRE) scenarios to derive future generator portfolios and hourly price and emissions series. The main objective of this exercise is to offer policymakers, utilities and grid authorities a long-range view of how current choices could impact their future ability to cope with changes in the electric sector.
In particular, simulations address generation mix, wholesale and ancillary service prices, and carbon emissions across SPP, NYISO, CAISO, and ERCOT in 2030. The modeling effort and the underlying simulations were led by an LCG expert team and conducted with LCG’s proprietary models including the long-term least-cost planning program, Gen-X, the integrated G&T market model, UPLAN-NPM, and the regional PLATO data models.
The study found a general decrease in average annual hourly wholesale energy prices with more VRE penetration, increased price volatility and frequency of very low-priced hours, and changing diurnal price patterns. Ancillary service prices rise substantially and peak net-load hours with high capacity value are shifted increasingly into the evening, particularly for high solar futures. A significant decrease in non VRE generation and a modest decrease of firm capacity need were observed for high VRE future. Figure below shows the mean diurnal (24h) energy price profiles by scenario and region, averaged over all weekdays.
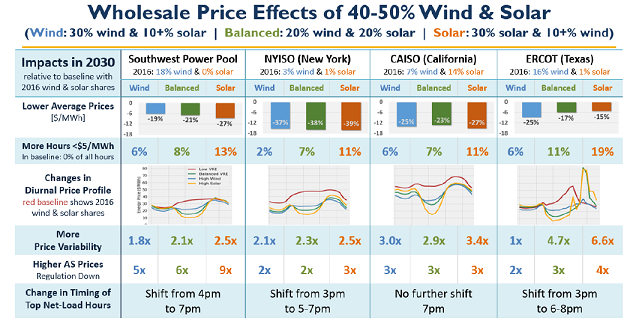
Source: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
The diurnal price profiles display the infamous duck curve in all regions for high solar case. The overall electricity prices for all VRE scenarios show a decline across all regions by $5 - $16/MWh with strong total price decline in NYISO, CAISO, and SPP for the solar case while ERCOT has the largest price reduction in the wind case. For the high VRE cases, the study observed substantial increase in low price hours. The annual share of low price hours where the prices are below $5/MWh varies from region to region from 2.5% to 19% for all hours of the year. These low price hours offer an opportunity for hybrid renewables and storage developers such as CAES, batteries, and load shifting programs to optimize their asset portfolios.
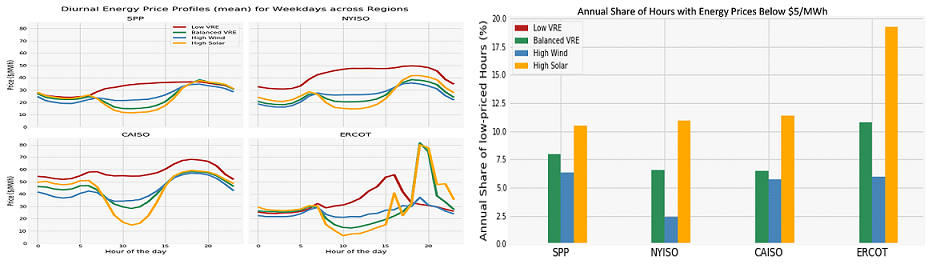
Source: LCG UPLAN-NPM simulation
The changes in the diurnal energy price profile, high ancillary service prices, and increased volatility may offer energy industry participants a new perspective for their future planning under alternative scenario. Hopefully, the study brings into focus how the current choices could impact their future ability to cope with changes in the electric sector.
Report (LBNL, LCG): http://eta-publications.lbl.gov/sites/default/files/report_pdf_0.pdf
Abstract, report and Data (LBNL): https://emp.lbl.gov/publications/impacts-high-variable-renewable
|
|
|
|
UPLAN-NPM
The Locational Marginal Price Model (LMP) Network Power Model
|
|
|
UPLAN-ACE
Day Ahead and Real Time Market Simulation
|
|
|
UPLAN-G
The Gas Procurement and Competitive Analysis System
|
|
|
PLATO
Database of Plants, Loads, Assets, Transmission...
|
|
|
|
|
